MEDA (Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer)
mission specific
Instrument Overview
The MEDA instrument consists of a suite of sensors and a control unit, packaged in eleven enclosures:
- Wind Sensor, WS (two detectors, WS1 and WS2, placed on two booms)
- Air Temperature Sensor, ATS (five detectors: three of them placed on the RSM, and two more at the front of the rover body)
- Thermal Infra-Red Sensor, TIRS
- Relative Humidity Sensor, HS
- Radiation and Dust Sensor, RDS (it also includes the SkyCam imager)
- Pressure Sensor, PS (inside the Instrument Control Unit, ICU)
The principal goal of this sensor suite is to provide continuous measurements that characterize the diurnal to seasonal cycles of the local environmental dust properties (opacity, size distribution, and phase function) and their temporal response to meteorology, and the local near-surface environment (pressure, air and surface temperature,relative humidity, wind, and solar radiative forcing in the UV-visible-IR parts of the spectrum). The figure below shows the MEDA sensors location onboard the rover.
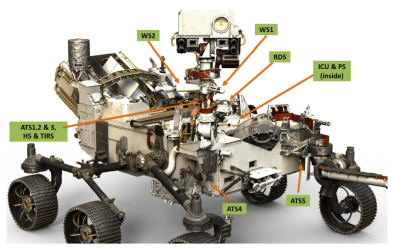
Location of MEDA Sensors onboard the Mars 2020 rover
The wind sensors are housed in two small Booms structures mounted orthogonal to the Remote Sensing Mast (RSM) of the Rover. Each Boom provides 6 wind sensor transducer boards on the head of the main boom cylinder. Booms include front-end mixed ASICs to condition and acquire the data from the wind sensors and to communicate serially with the Instrument Control Unit (ICU). This minimizes the number of cables required.
The Thermal-Infrared Radiation Sensor (TIRS) is also mounted on the RSM and it is composed of 5 thermopiles pointing upward and downward to measure different ground and atmosphere temperatures in different infrared bands and the solar radiation reflected on the ground (albedo).
The Humidity Sensor (HS) is directly mounted to the RSM as well. It contains up to three capacitive sensor heads sensitive to the ambient relative humidity. The figure below shows the relative positions of all of the sensors located on the RSM.
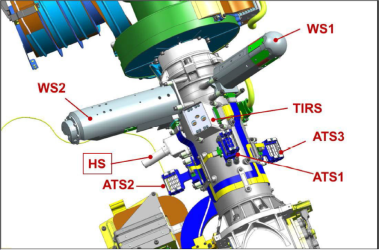
Wind sensors, air temperature sensors 1 to 3, thermal infrared sensor, and humidity sensor on the RSM.
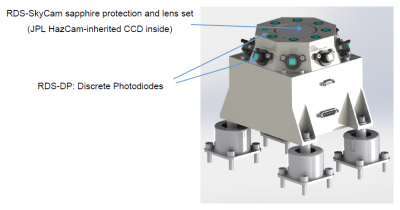
The Radiation and Dust sensor (RDS) is mounted on the rover top deck and comprises of eight upward viewing UV photodetectors (8 photodiodes), 8 lateral viewing UV photodiodes (every photodiode looking 45º apart from the previous to cover the full 360º around the unit), a reference dark-current photodiode and an upward looking camera (see figure below). The signals coming from these photodiodes and thermopiles will be routed to the ICU to be conditioned and digitized inside the ICU. The ICU will also control the camera through its power and data interfaces.
The instrument control unit, the ICU, is mounted upside-down to the Rover Avionics Mounting Panel (RAMP), inside the rover chassis just under the top deck. It plans and controls the sensors’ data acquisition, communicating with Rover Computer Element (RCE) and temporarily storing science and housekeeping data.
The pressure sensor (PS) is located with the ICU analog module but additionally uses a small tube to reach the Martian environment outside the rover. This tube passes through the ICU base plate, the RAMP, and into a cavity in the rover top deck. The opening is protected from dust and for planetary protection reasons by a cover that attaches to the rover top deck .
The instrument will regularly make measurements throughout the Martian day and night, over the lifetime of the Mars 2020 mission. To achieve these measurements, MEDA is designed primarily to operate from an autonomous, low-power “sleep” mode, which can be powered even while the RCE is off. An internal timer wakes MEDA to take observations according to a predetermined schedule, saves the data internally, and goes back to sleep. Instrument housekeeping tasks can also be performed to a schedule.
MEDA Sky Camera
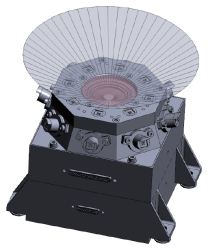
The MEDA Skycam is a fixed camera looking up, which is intended to take images of the sky for weather monitoring purposes. It is a build-to-print copy of the MER and MSL Engineering Cameras (but with a different lens). See the table below for camera characteristics. The camera is mounted in the center of the Radiation and Dust Sensor (RDS) and also includes a 120º FOV Baffle (ring on lens) that will be used to block sunlight at specific times during the Martian Sol (see figure below).
| SkyCam Operational Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Value |
| Resolution (S x L) | 1024 x 1024 |
| Bit Depth | 12 |
| Field of View (FOV) | 124 x 124 deg |
| Angular Resolution | 2.1 mrad/pixel at center |
| Spectral Bandpass | 600 - 800 nm |
| Focal Length | 5.58 mm |
| f/number | 15 |
| Depth of field | 0.1 m - infinity |
| Best focus | 0.5 m |